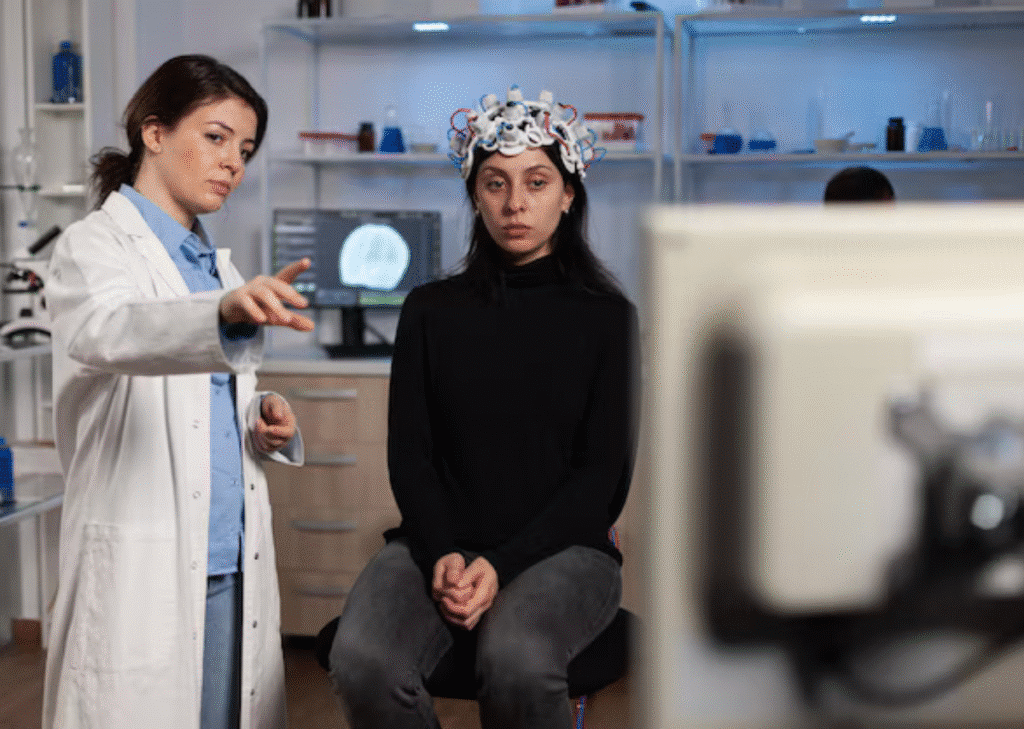
Introduction
EMDR therapy might have crossed your path in case, somehow, you have suffered emotional trauma or have issues with PTSD. EMDR therapy which is also known as Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing is a revolutionary type of therapy which assists the sufferer to get over traumatic experiences. In contrast to the usual talk therapy, EMDR therapy involves the use of certain techniques such as guided eye movement to reprocess traumatic memories to render them less emotionally charged. It is regarded to be one of the best therapies in relation to PTSD, anxiety and trauma related disorders.
This is a broad guide through which we will discuss the working mechanism of EMDR therapy, its different advantages and its efficiency in managing mental health conditions. No matter whether you are thinking about taking the therapy yourself or what you just want to learn about the therapy, continue to read this to know why EMDR therapy is becoming a reliable option among the people who want to recover traumatic experiences of the past.
What is EMDR Therapy?
EMDR therapy is a form of therapy that has been established to assist people to process and heal traumatic memories. EMDR therapy was developed in the late 1980s by a doctor, Francine Shapiro, and nowadays is an extensively used evidence-based therapy applicable to PTSD, anxiety, depression, and other mental conditions. EMDR is fundamentally based on the idea that traumatic memories that do not get processed in an appropriate fashion stick in the brain and give rise to emotional and psychological disturbances.
EMDR treatment involves the process of bilateral stimulation (usually with the use of tapping or eye movements) of the brain and remembering traumatic memories on both sides. This assists the brain to reprocess and store these memories in a more healthy fashion. Consequently, the emotional load of the memory is reduced, and the individual will be able to perceive the event without any emotional attachment, which will result in the alleviation of the symptoms.
How Does EMDR Therapy Work?
EMDR therapy process entails eight phases. All the stages are meant to help the individual heal through traumas in a manner that will lead to long-term recovery.
1. History Taking and Treatment Planning.
The initial stage entails a deep dialogue between the therapist and the client. The therapist collects data regarding the past trauma of the client, the symptoms and history of mental health of the client. This assists the therapist to develop a tailor made treatment strategy that is based on the unique needs of the client.
2. Preparation
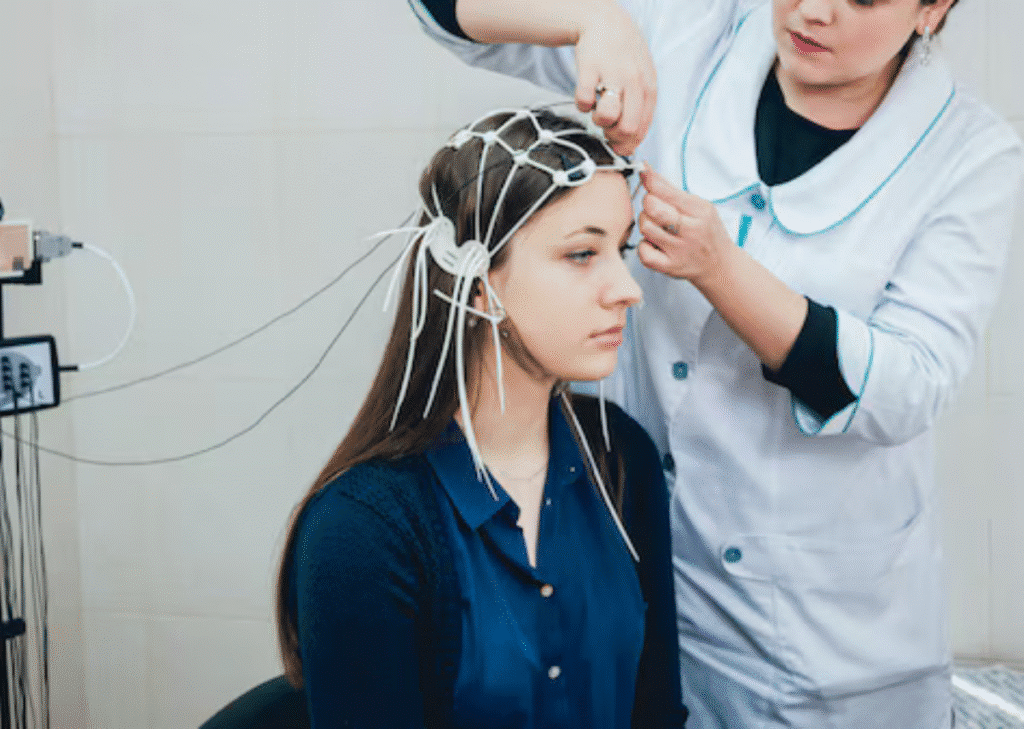

During the preparation stage, the therapist informs the client about the EMDR therapy process, making expectations about the treatment. The therapist provides the client with the way forward, and they are at ease with the practice. Relaxation methods used in coping are learned in this stage to enable coping with any distress that might come.
3. Assessment
When it is time to conduct the assessment, the client is requested to concentrate on a certain traumatic memory. The therapist makes the client realize the negative beliefs associated with it (e.g., I am powerless) and chooses a positive belief (e.g., I am strong) that she is going to use instead. The client will be requested to rank the emotional intensity of the memory to monitor the progress.
4. Desensitization
During the desensitization stage, bilateral stimulation is applied. This is usually in the form of the client tracking the movements of the hands of the therapist or hearing backward and forward sounds. The bilateral stimulation of both hemispheres of the brain with the assistance of this method will help to re-process the traumatic memory and make it less emotional.
5. Installation
When the emotional value of the memory is diminished then the emphasis is given to the reinforcement of the positive belief that has been identified earlier. The therapist does bilateral stimulation to make the client install the new empowering belief to make them feel stronger and more resilient.
6. Body Scan
The body scan is the process whereby the client will scan his or her body on any pending tension, and discomfort associated with the memory. In case of occurrence of any physical sensations, the therapist then resorts to bilateral stimulation as a way of releasing these tensions, which leads to a feeling of physical and emotional relaxation.
7. Closure
The therapist has to make sure that the client is grounded and emotionally stable at the end of every session. The use of relaxation techniques can be common to make the client get to a neutral position before moving out of the session. This is necessary to maintain that the client is not overwhelmed with the processing of difficult memories.
8. Reevaluation
In the next sessions, the therapist checks with the client on the progress achieved and revisits the memories that were worked on in the earlier sessions. In case any new concerns or unheard memories are noted, they are resolved in the following sessions.
What Are the Benefits of EMDR Therapy?
EMDR therapy is very advantageous and hence this form is very useful in the treatment of trauma, PTSD, and other emotional issues. The greatest benefits of this treatment are the following:
1. Efficient with PTSD and Trauma.
EMDR therapy has largely been considered to be one of the most effective treatment of PTSD. Coming at traumatic memories in an organized and treatment-oriented manner enables the EMDR treatment of traumatized people to minimize the emotional intensity of distraught memories, and eventually enables the traumatized individual to overcome the trauma.

2. Faster Benefits than Conventional Therapy.
The EMDR therapy can relieve faster than the traditional treatment, which may take months or even years before producing substantial outcomes. It is also a popular choice among patients who want to experience faster emotional recovery because, in most cases, they feel significantly improved after several sessions.
3. Non-Invasive
The fact that EMDR therapy is non-invasive is one of the most appealing aspects about the treatment. The EMDR therapy has no physical intervention like other treatment approaches, including medication or surgery. It depends on the techniques of the mind such as bilateral stimulation to enable the brain to recover on its own.
4. Handles a Large Area of Concerns.
EMDR therapy is very effective in a wide range of mental health complications, such as anxiety, depression, phobias, and even performance anxiety, although it is mostly applied to the treatment of PTSD. Such flexibility makes it a desirable alternative to people who have to address diverse emotional and psychological issues.
5. Long-Term Effectiveness
EMDR therapy has a lot of positive effects which tend to remain long after one has stopped treatment. Since the therapy is aimed at the cause of distress (traumatic memories), it may result in permanent emotional recovery. A long-term reduction of symptoms is observed in many patients despite the end of treatment.
Is EMDR Therapy Effective?
Yes, EMDR therapy is widely studied and has been found to be very effective in the treatment of PTSD and other trauma related disorders. The clinical research has shown that the EMDR therapy results in a substantial drop in the symptoms of PTSD, anxiety, and depression. Major mental health organizations have approved the treatment as an evidence-based trauma treatment including the American Psychological Association (APA) and the World Health Organization (WHO).
Most people report a lot of improvement after some few sessions although individual outcomes can be different. More sessions might be required to deal with deeper or more complicated traumas, but most patients claim to have made significant improvements.
Conclusion:
EMDR is an effective and workable method of emotional trauma healing, PTSD, anxiety and other mental health disorders. Its special technique of bilateral stimulation to re-process the unpleasant memories has rendered it one of the most viable therapies in trauma reclamation. EMDR therapy provides an option to heal and control your life whether you are confronted with the past trauma or whether you are caught up with the present emotional pain.
EMDR therapy is a non-invasive alternative that can assist the person of any origin in seeking relief due to its capacity to give faster outcome than traditional therapies and its long-term advantages. EMDR therapy can be the solution, as long as you are willing to heal previous traumas and be able to move on to emotional health. Talk to an experienced therapist and consider how this transformational therapy can assist you to resolve your issues and lead a healthier and more balanced life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the time taken before EMDR therapy works?
EMDR therapy may take different periods of time before results are seen. An overwhelming majority of patients feel better in 6-12 sessions. Nevertheless, others can experience quicker changes, whereas other individuals with more complicated trauma might need more sessions.
Is EMDR therapy painful?
EMDR treatment is not painful and may arouse strong emotions during the processing of traumatic memories. Your therapist will help you to go through the process so that you feel supported.
Is EMDR therapy appropriate in children?
EMDR therapy is adjustable to children, and more so, those who are exposed to trauma. To make children participate in the process, therapists can apply imaginative techniques such as art or storytelling.
What are the side effects of EMDR therapy?
The majority of patients do not have any long-term side effects of EMDR therapy. Nevertheless, others can experience short-lasting emotional distress or intense dreaming when working on their memories. These are side effects that usually fade away after the session.
EMDR therapy is insurable?
EMDR therapy is frequently included in the insurance coverage of many insurance companies, especially when applied to address traumatic-related diseases such as PTSD. It is always a good idea to call on your insurance provider to clarify on the coverage prior to commencing treatment.





